
FAST FACTS: Eye Pain
Eye pain and visual damages can be associated with serious health issues for older adults, including limitations in physical activity, impaired mobility, and poor balance which can lead to falls or fractures. Assessment of common eye conditions in older adults is crucial to having positive outcomes. Many eye disorders share common symptoms such as some degree of eye pain or discomfort and eye redness.
Normal Changes of the Aging Eye
- Tear production decreases which may cause dry eyes
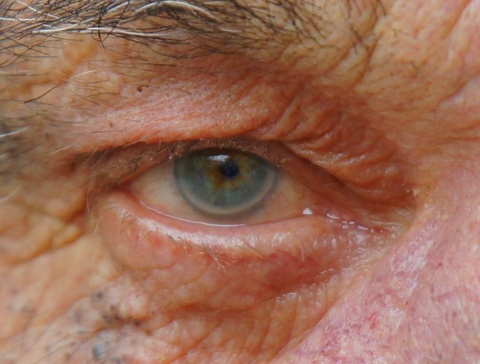
- A gray-white ring can form around the “colored” part of the eye; there is no significance to this (see photo on right)
- Sensitivity to touch decreases so the eye can be more easily scratched, and the cornea injured
- Overall sensitivity of the eye decreases as we age which may lead to damage to the cornea
- “Floaters” are specks or spots in vision and are common
- Pupil size deceases and reaction to light and dark is slower.
Assessment
- Recognition is critical. All eye complaints deserve immediate assessment to preserve vision and avoid complications
- What to report to healthcare provider:
- Information about the reported pain such as: when it started, location, how long, severity, foreign body sensation, and anything else your loved one mentions
- Potential causes of the pain such as: foreign object in eye, trauma, allergies
- Other symptoms such as: fever, visual complaints, headache, nausea, not eating, fatigue, dizziness, cough, change in cognitive status.
Possible Intervention
- Will depend on the results of assessment by your loved one’s healthcare provider
- Non-Drug Treatments include maintaining a calm environment, reassuring the patient, and providing support as needed to maintain safety
What Else You Should Do
- Write down and share information about your loved one’s pain with their healthcare provider
- Use a Pain Diary to note important information useful to the healthcare provider
- Encourage your loved one to try a non-drug treatment and document the impact on their pain in their Pain Diary
References:
- Mayo Clinic. March 11, 2021. Eye pain. Accessed 3.13.2022. https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/eye-pain/basics/causes/sym-20050744
- WebMD. August 26, 2020. Eye Pain: What Are the Causes? Accessed 3.13.2022. https://www.webmd.com/eye-health/eye-pain-causes-symptoms-diagnosis-treatment
- Cleveland Clinic. May 3, 2018. Eye Pain. Accessed 3.13.2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/17796-eye-pain
Revised January 2022
